-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
-
Flow Cytometry Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
- Single Cell Multiomics Reagents
-
Cell Preparation
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
- Western Blotting And Molecular Reagents
- Cell Preparation Separation Reagents
- Functional Cell Based Reagents
- Microscopy Imaging Reagents
- Single Cell Multiomics Reagents
- Single Cell Multinomics Reagents
-
Protocols
- BSB Protocol
-
Setting Compensation Multicolor Flow
-
Tissues Section Stain
-
Immunomicroscopy
-
Immunohistochemical
-
Immunofluorescence
-
Frozen Tissue
-
Parafin Sections
-
Fix Perm Kits
-
Protocol Direct Immunofluorscence Staining
-
Uses of Fc Block
-
Stain Lyse Wash
-
Stain Lyse No Wash
-
Mouse Splenocytes
-
Mouse Rat Leukocytes
-
Isotype Control
-
Indirect Staining Mononuclear Cells
-
Immunopurification
-
Human PBMCs
-
Human Whole Blood Samples
-
Escapee Phenomenon
-
Agarose Conjugates
-
Anti Phosphotyrosine Biotin Conjugates
-
Soluble Antibodies
-
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibodies
-
Monocloncal Antibodies
-
Horseradish Peroxidase
-
Certified Reagents
-
Biotinylated Antibodies
-
Agarose Conjugates X712261
-
Surface Staining
-
Platelet Activation
-
Intracellular Staining
-
Indirect Immunofluorescence
-
Mouse Ige
-
Cytokine Elisa
-
Induction Fas
-
Induction Dx2
-
Apoptosis By Treatment Staurosporine
-
Cell Death
-
Apo Brdu
-
Apo Direct
-
Human Cyclins
-
Detection Ki 67
-
Brdu Detection
-
Targeted mRNA Protocols
-
WTA Protocols
-
360040667732 Protocols
-
360023293831 AbSeq Protocols
-
360039007471 VDJ CDR3 Protocols
-
Annexin V Staining Protocol
-
Western Blotting with Horseradish Peroxidase Conjugates or Alkaline Phosphatase Conjugates
-
Tissue Preparation for Surface Antigen Staining
-
Account Support
-
Account FAQs
- Account FAQ Answer 1
- Account FAQ Answer 2
- Account FAQ Answer 3
- Account FAQ Answer 4
- Account FAQ Answer 5
- Account FAQ Answer 6
- Account FAQ Answer 7
- Account FAQ Answer 8
- Account FAQ Answer 9
- Account FAQ Answer 10
- Account FAQ Answer 11
- Account FAQ Answer 12
- Account FAQ Answer 13
- Account FAQ Answer 14
- Account FAQ Answer 15
- Account FAQ Answer 16
- Account FAQ Answer 21
- Create Account
- Manage Account Settings
-
PrivacyPolicy
-
Terms and Conditions
-
Account FAQs
-
- Account FAQ Answer 1
- Account FAQ Answer 2
- Account FAQ Answer 3
- Account FAQ Answer 4
- Account FAQ Answer 5
- Account FAQ Answer 6
- Account FAQ Answer 7
- Account FAQ Answer 8
- Account FAQ Answer 9
- Account FAQ Answer 10
- Account FAQ Answer 11
- Account FAQ Answer 12
- Account FAQ Answer 13
- Account FAQ Answer 14
- Account FAQ Answer 15
- Account FAQ Answer 16
- Account FAQ Answer 21
- Korea (English)
- Korea (Korea)
-
국가 / 언어 변경
Old Browser

Cell Proliferation
Multiple stimuli, such as cytokine treatment, can affect cell proliferation. Cell proliferation can occur in response to many stimuli such as cytokine exposure or a variety of other processes.
Cell proliferation dyes
BD Biosciences offers BD Horizon™ Violet Proliferation Dye 450 (VPD450) and BD Horizon™ CFSE for the detection of cell proliferation with the violet laser and blue laser, respectively, which facilitates the use of larger panels. This allows the determination of more data from limited samples using multicolor flow cytometry. Both proliferation dyes are nonfluorescent esterified dyes. The ester group allows the dye to enter the cell. Once the dye is inside the cell, esterases cleave off the ester group to convert the dye into a fluorescent product and trap it inside the cell. With each replication event the amount of dye in the cell is decreased, leading to a characteristic pattern.
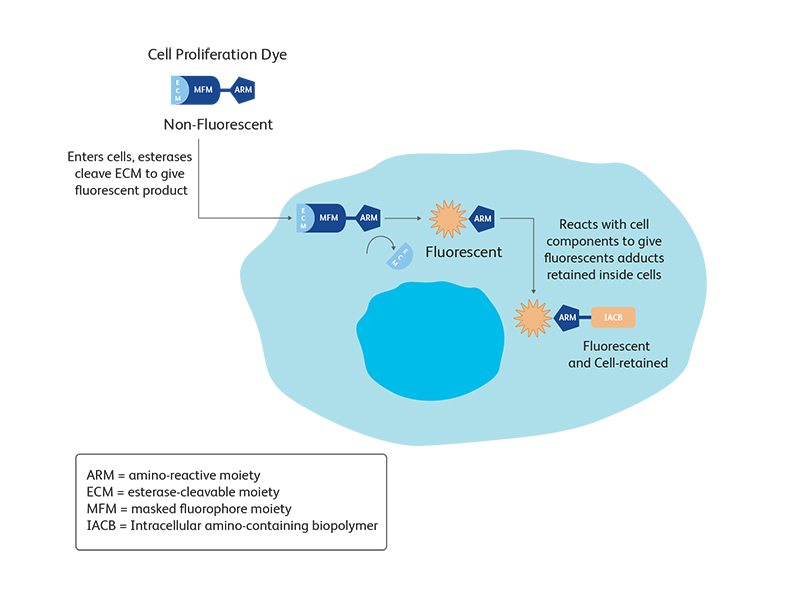

BD Horizon™ Cell Proliferation Dyes freely enter a cell. Once inside the cell, the dyes are cleaved by nonspecific esterases and release a fluorescent molecule, which becomes trapped inside the cell. Concentration of VPD450 and cell-cycle kinetics on mouse spleen stimulated with antiCD3e and anti-CD28. C57 Black/6 splenocytes were either loaded with varying concentrations of BD Horizon™ VPD450, DMSO, or left as untreated controls, then stimulated with anti-CD3e and anti-CD28 for two days. Cells were pulsed with BrdU prior to harvesting, then stained with APC anti-BrdU and 7-AAD (Cat. No. 552598). The top panels (A–C) illustrate APC antiBrdU and 7-AAD staining. The bottom panels (D–F) illustrate the corresponding VPD450 histograms. The control cells (Cells– ) (Panel A) and the 1-μM VPD450- loaded cell population (Panel C) demonstrated a similar percentage of BrdU+ cells (40.7% and 39.8%, respectively). Higher concentrations of dye can negatively impact cell proliferation (data not shown). To confirm that the DMSO (which is used as a solvent for VPD450) is not responsible for a decrease in proliferation, a DMSO group was included (Panel B). DMSO-treated cells incorporated a similar percentage of BrdU compared to the Cells– group and the 1-μM VPD450-loaded cell populations.
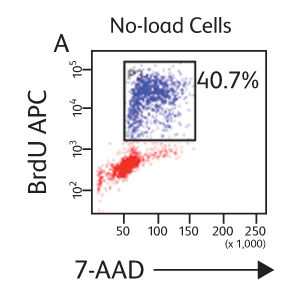
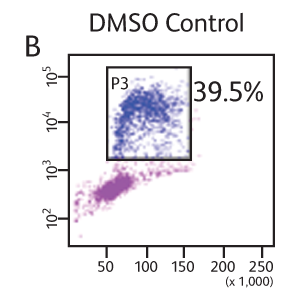
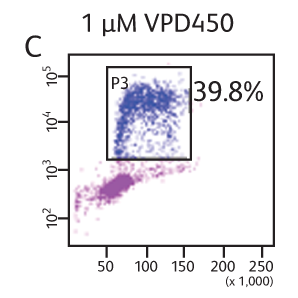
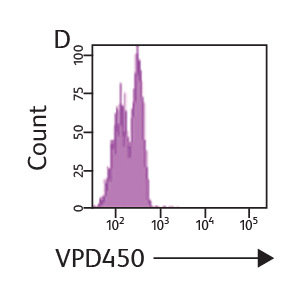
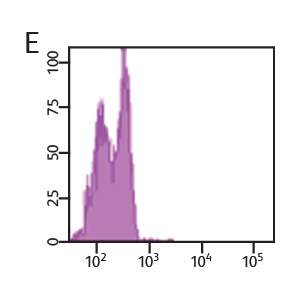
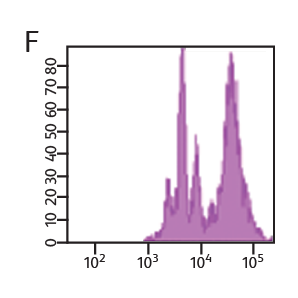
Concentration of VPD450 and cell-cycle kinetics on mouse spleen stimulated with antiCD3e and anti-CD28. C57 Black/6 splenocytes were either loaded with varying concentrations of BD Horizon™ VPD450, DMSO, or left as untreated controls, then stimulated with anti-CD3e and anti-CD28 for two days. Cells were pulsed with BrdU prior to harvesting, then stained with APC anti-BrdU and 7-AAD (Cat. No. 552598). The top panels (A–C) illustrate APC antiBrdU and 7-AAD staining. The bottom panels (D–F) illustrate the corresponding VPD450 histograms. The control cells (Cells– ) (Panel A) and the 1-μM VPD450- loaded cell population (Panel C) demonstrated a similar percentage of BrdU+ cells (40.7% and 39.8%, respectively). Higher concentrations of dye can negatively impact cell proliferation (data not shown). To confirm that the DMSO (which is used as a solvent for VPD450) is not responsible for a decrease in proliferation, a DMSO group was included (Panel B). DMSO-treated cells incorporated a similar percentage of BrdU compared to the Cells– group and the 1-μM VPD450-loaded cell populations.
Measurement of cell proliferation with BrdU
BD Biosciences carries a series of antibodies and kits designed for the detection of proliferating cells by measurement of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU), an analog of the DNA precursor thymidine used to measure de novo DNA synthesis.
During the S phase of the cell cycle (DNA synthesis), BrdU is incorporated into the newly synthesized DNA and can be readily detected by anti-BrdU specific antibodies. BD antibodies and kits designed for the detection of BrdU are available for both intracellular flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry and include BD Horizon™ V450, BD Horizon Brilliant Violet™ 510 (BV510), PerCP-Cy5.5 and other formats.
In addition to DNA increases, levels of certain proteins also rise as a result of cell proliferation. For example, Ki67 is an antigen that is expressed in the nucleus of dividing cells. However, during the G0 phase of the cell cycle, it is not detected. Ki67 can be combined with other proliferation markers such as BrdU and VPD450 for added confidence. These markers can also be combined with cell surface and other types of markers to gain additional information about cell subsets and their signaling pathways.
Cell proliferation analysis of mouse splenocytes
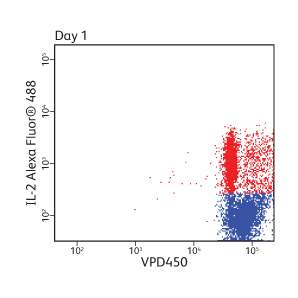
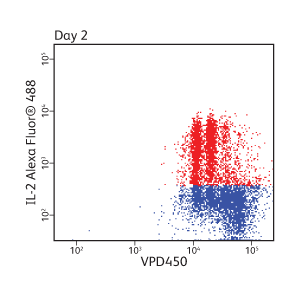
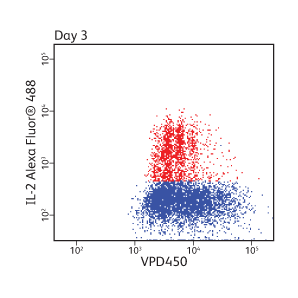
CD4+ enriched mouse splenocytes were loaded with 1 µM VPD450 for 10 minutes. Cells were then stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 and harvested at the indicated times. Approximately 4 to 6 hours prior to harvest, cells were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin in the presence of BD GolgiStop™ Protein Transport Inhibitor. Cells were fixed and permeabilized, stained for IL-2, and analyzed on a BD® LSR II Flow Cytometer.
-
Application Notes
-
Brochure
-
Product Information Sheets
-
Product List
-
Webinars
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
BD flow cytometers are Class 1 Laser Products.
Alexa Fluor is a trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
Cy is a trademark of Global Life Sciences Solutions Germany GmbH or an affiliate doing business as Cytiva.
23-23094-00
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.